The Evolving Digital Landscape and Cybersecurity Threats in 2024
As we navigate through 2024, the digital landscape continues to evolve at an unprecedented pace. Innovations in technology—ranging from artificial intelligence and machine learning to the expansion of the Internet of Things (IoT)—are reshaping how we interact, work, and conduct business. However, with this rapid progress comes an ever-growing array of cybersecurity threats that pose significant risks to both individuals and organizations alike.
The Escalating Threat Landscape
Cybersecurity attacks are becoming increasingly sophisticated and varied, with malicious actors employing advanced tactics to exploit vulnerabilities in systems and networks. In recent years, we have witnessed a shift from traditional threats to more complex, multi-layered attacks that can easily bypass standard security measures. As technology advances, so do the methods used by cybercriminals, making it crucial for everyone to stay informed about potential risks.
In 2024, cybersecurity threats have manifested in various forms, including ransomware attacks, phishing schemes, data breaches, and more. Each type of attack presents unique challenges and can have severe consequences, ranging from financial loss to reputational damage and even legal ramifications. This complexity underscores the need for heightened awareness and proactive measures to defend against these evolving threats.
The Importance of Staying Informed
Awareness is the first line of defense against cybersecurity threats. Individuals and organizations must educate themselves about the current threat landscape, recognizing the signs of potential attacks and understanding how to respond effectively. Cybersecurity training and resources are essential in empowering employees and users to make informed decisions about their online activities and to identify potential red flags.
In this blog post, we will explore the top 25 cybersecurity attacks that have made headlines in 2024. Each case will provide insights into the nature of the attack, the methods employed by cybercriminals, and the impact on the targeted individuals or organizations. By analyzing these incidents, we aim to equip readers with valuable knowledge to better protect themselves and their digital assets.
Master the Art of Cybersecurity
Ready to kickstart your cybersecurity career? Enroll with GradeSpot IT Solutions and gain the skills needed to land your dream job in cybersecurity!
1. Ransomware Attacks:
Typically, ransomware is a type of cyber attack whereby a threat actor uses malware to encrypt data or lock a person out of their system. Usually, once the ransomware is activated, the attackers start demanding money in the form of cryptocurrency that will enable them to give the decryption key or access back to their data. In addition, ransomware-as-a-service also means that even pretty unsophisticated cybercrooks can now carry out ransomware attacks for anyone without having to write their own ransomware. Of course, the ransomware attack vector apparently hits from solitary victims to multinational companies and, interestingly, government institutions as well-meaning ransomware is indeed all-rounded.
Damaging effects of ransomware attacks will include high monetary loss, loss during the operational downtime, and reputational damage. Apart from financial demands, usually, there’s a threat to release confidential information in case of the failure to pay ransom, which adds pressure on the victim to comply. Highly valuable sectors, such as health, finance, and energy, are now targeted by ransomware groups who have become more organized due to the changing threat landscape nature. To curb such an attack, an organization needs to be proactive about its cybersecurity strategy as regular data backup, making the employees aware of such matters, and layered defense in the protection against an attack on vulnerability and scope.
2. Phishing Attacks:
The attackers normally forward fake or deceitful e-mails or SMSes or phishing websites pretending to be one of the trusted service providers, banks, shopping sites, or even government agencies, and they attempt to phish people by sending them deceitful requests for sensitive information including login information, account numbers, and even financial information. The phishing attack makes an attempt to get the receiver to click on a link with some harmful attachments or provide his private information on a fake website. So, phishing often takes the form of one of the simplest attacks and therefore the most effective ones in the domain of cyberattacks.
Phishing attacks have become more sophisticated and harder to detect over time, often leveraging social engineering to craft convincing, personalized messages. Attackers may use information from social media or public records for spear-phishing, targeting specific individuals. Phishing now extends beyond emails to include SMS-based attacks (smishing), phone calls (vishing), and social media scams. To effectively combat phishing, individuals must stay vigilant, verify the authenticity of messages, and use security tools such as email filters and multi-factor authentication.
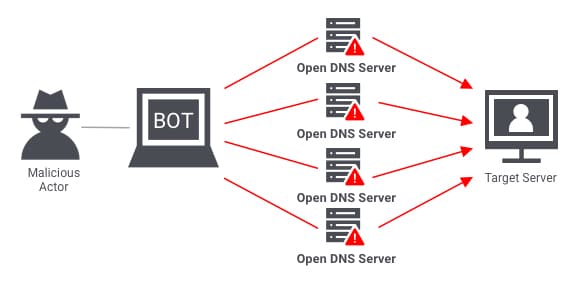
3. Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks:
A DDoS attack is a type of cyber attack that utilizes malware to start interference with normal operations of a target, typically any website, server, or network, by suddenly sending an abnormal volume of internet traffic to the target. Unlike traditional Denial of Service attacks where one compromised device floods a target, DDoS uses multiple compromised devices, popularly termed a botnet, and it does this all at once. This distributed nature makes DDoS attacks hard to mitigate since the traffic is masked by many legitimate sources that it seems to be coming from.
Such an attack can be very damaging if it is successful as it often causes extended downtime, loss in revenue, and harm to the reputation of an organization. Finance to health care, which could serve customers, or to access much-needed resources would have candidates to target. Organizations use many mitigations, including traffic filtering and rate limiting, as well as using specialized DDoS protection services that detect and neutralize attack traffic before reaching the target. As DDoS tactics have developed to become ever more sophisticated scenarios with large volumes, so too have fences and barriers. Stricter defense systems, scalable, are needed.
4. Insider Threats:
An insider attack involves an individual within an organization—such as an employee, contractor, or partner—compromising security, either intentionally or accidentally. Since these attackers have legitimate access to sensitive data and systems, defending against them is particularly challenging. Insider threats can range from deliberate actions like data theft or sabotage to unintentional incidents like accidental data exposure or falling victim to phishing. These attacks are often highly damaging, as they exploit trusted access, making detection difficult with traditional security methods. To mitigate such risks, organizations must combine technical controls, behavioral monitoring, and strong security policies.
Insider threats are like a wolf in sheep's clothing. They're people who work for a company but use their access to harm it. It could be a disgruntled employee stealing trade secrets out of spite, a careless worker accidentally sharing confidential information, or even a well-meaning contractor who makes a mistake. These threats can be hard to spot because they come from within, and they can cause serious damage.
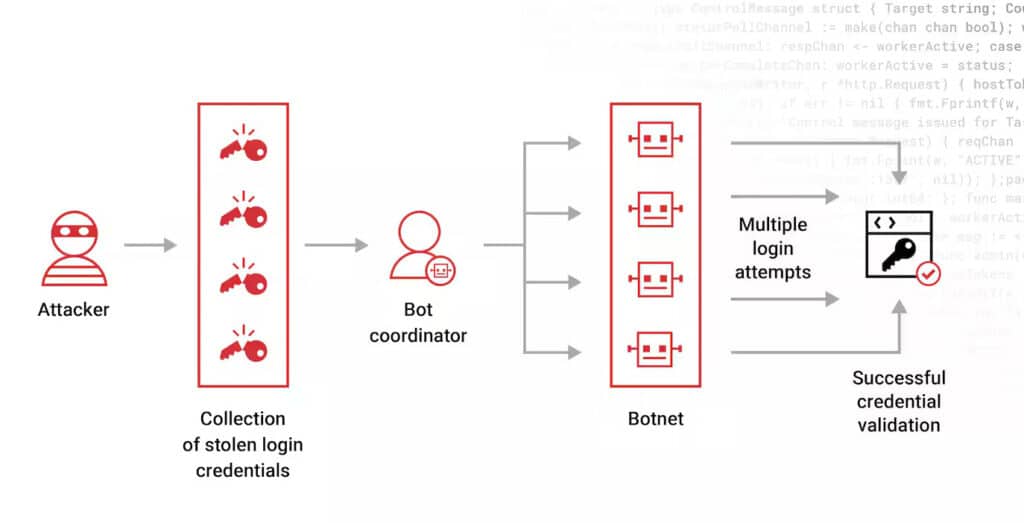
5. Credential Stuffing Attacks:
A credential stuffing attack is a type of cyber attack where the hackers perform massive logins on different platforms online by using their automated tools and logins accessed from previous data breach windows. Since many people reuse the same credentials across multiple accounts, attackers can exploit this practice by trying these stolen login details on a wide range of websites and services. After the successful access, the attackers, through logging, will have unauthorized access to users’ accounts due to data theft or financial losses or any malicious activity. They are advised to use a unique and very strong password for each account, other than enabling Multi-factor authentication or MFA.
6. Internet of Things (IoT) Vulnerabilities:
The Internet of Things (IoT) connects everything from smart home devices to industrial machinery, but with that convenience comes a downside: many of these devices aren’t designed with strong security in mind. They often come with weak or default passwords and limited processing power, which makes them easy targets for cybercriminals. Hackers take advantage of these weaknesses to break into devices, sometimes using them to launch larger attacks like DDoS or to access private networks and steal data. As the number of IoT devices continues to grow, the risk increases, which means we all need to prioritize better security practices—such as regularly updating devices, using strong passwords, and keeping networks segmented—to protect against these vulnerabilities.
7. Artificial Intelligence (AI)-Driven Attacks:
AI-driven attacks are a growing cybersecurity threat, utilizing artificial intelligence to enhance the sophistication of cyberattacks. These threats can automate phishing campaigns, find system vulnerabilities, and execute highly personalized social engineering, making them difficult to detect. AI-powered malware can adapt to its environment, bypassing defenses more effectively. As attackers exploit AI, defenders must also leverage it to stay ahead of these evolving threats.
AI is making cyberattacks more sophisticated and harder to stop. Attackers use AI to automate phishing, find weaknesses in systems, and even trick people into giving up their information. AI-powered malware can also learn and adapt to avoid security measures. To stay safe, defenders must also use AI in their security tools.
8. Zero-Day Exploits:
A Zero-Day exploit is an unidentified flaw in the software or hardware such that it is unknown to the developers or even the vendors responsible for the system. Since they are unaware of the flaw, they have had “zero days” to correct the bug. It’s a perfect opportunity for attackers to exploit. The exploits of Zero-Day fall generally into the group of infiltration by cyber-criminals without a chance of installing protective measures in place that can counter and prevent attacks, making Zero-Day exploits highly dangerous. It may target any operating system, application, or even firmware, and its exploitation could expose both an individual and an organization until the vulnerability is patched.
9. Social Engineering Attacks:
Social engineering attacks manipulate people into revealing sensitive information or taking actions that compromise security. Rather than targeting technical vulnerabilities, these attacks exploit human psychology, often employing tactics like impersonation, deception, and urgency to create feelings of trust or fear. For example, an attacker might pose as a trusted colleague or a legitimate service provider, sending seemingly harmless emails that contain links to malicious websites. These manipulative strategies can lead victims to unknowingly disclose critical information, such as passwords or financial details, resulting in devastating consequences. Understanding the emotional triggers behind these attacks is essential for recognizing and preventing them, empowering individuals to protect themselves and their sensitive data.
10. Malware Attacks:
Malware attacks involve malicious software designed to infiltrate, damage, or disable computers and networks, often without users’ awareness. They take many forms, including viruses, worms, Trojans, ransomware, and spyware, each with unique methods and goals. For instance, ransomware locks users out of their files until a payment is made, while spyware stealthily collects sensitive information about their activities. The emotional impact of these attacks can be profound, leaving individuals and businesses feeling vulnerable and exposed as they deal with financial losses, data recovery, and diminished trust in their technology. As technology evolves, it’s essential to understand and combat these cyber threats to ensure a safe and seamless digital experience.
11. Business Email Compromise (BEC):
Business Email Compromise (BEC) attacks are a sophisticated form of cybercrime where attackers impersonate a trusted entity, often through email, to manipulate employees into making unauthorized transactions or divulging sensitive information. These scams usually begin with extensive research on the target organization, allowing criminals to craft convincing messages that appear legitimate. For instance, an attacker might pose as a company executive or a trusted supplier, urging an employee to transfer funds or share confidential data. The impact of BEC attacks can be devastating, leading to significant financial losses and eroding trust within an organization, highlighting the critical need for vigilance and comprehensive employee training in cybersecurity awareness.
12. Credential Harvesting:
Credential harvesting is a sneaky tactic used by cybercriminals to steal your sensitive information, like usernames and passwords. Imagine receiving an email that looks like it’s from your bank or a favorite online store, urging you to log in and confirm your details. When you click the link and enter your information, thinking you’re being cautious, you might unknowingly hand over your credentials to an attacker. This can lead to serious consequences, including identity theft or financial loss. In a world where we rely on digital platforms for everything, it’s crucial to stay alert and recognize the signs of such scams, helping protect ourselves and our personal information from those who would take advantage of our trust.
13. Domain Spoofing:
Domain spoofing is a sneaky tactic used by cybercriminals to trick people into thinking they’re dealing with a trustworthy website. Imagine receiving an email that looks just like it’s from your bank, complete with logos and familiar language, prompting you to click a link to log in. However, that link leads to a cleverly disguised fake site designed to steal your personal information, like your passwords or credit card numbers. This form of deception exploits our natural trust in familiar brands, emphasizing the importance of staying alert and double-checking URLs before entering sensitive information. By understanding this threat, we can better protect ourselves and our personal data from being misused.
Here's a simple analogy: Imagine you're waiting for a package. You receive a text message with a link claiming to be from the delivery service, asking you to track your package. If you click the link and it takes you to a fake website, you might unknowingly provide your personal information, thinking you're interacting with the legitimate company. This is domain spoofing in action.
14. Data Breaches:
A data breach occurs when someone gains unauthorized access to sensitive information, such as personal details, financial data, or proprietary business information. Imagine waking up to find out that your private information has been compromised—this can lead to a whirlwind of emotions, from fear to anger. Individuals may face the anxiety of identity theft and the burden of dealing with potential financial losses, while organizations can suffer reputational damage and loss of customer trust. The impact of a breach extends beyond just numbers; it affects lives, relationships, and peace of mind. As we navigate an increasingly digital world, it’s crucial to prioritize our security and take steps to protect our valuable information.
15. Cyber Espionage:
Cyber espionage is like the digital version of spying, where individuals or organizations sneak in to steal sensitive information without permission. Imagine skilled hackers or even government-backed teams working behind the scenes, quietly infiltrating networks to uncover secrets that could give them a competitive edge or crucial intelligence. Unlike traditional spies who might physically sneak into buildings, these cyber intruders use the internet to exploit weaknesses in security systems, often without leaving a trace. The consequences can be significant—stolen data can undermine national security, lead to corporate theft, and damage trust among people and institutions. This highlights the urgent need for strong cybersecurity practices to safeguard our valuable information in today’s connected world.
16. Data Exfiltration Attacks:
Data exfiltration attacks happen when cybercriminals sneak into a system and steal sensitive information, often without anyone realizing it. Picture someone breaking into a house while the owners are asleep, quietly taking valuables and slipping away. In the digital world, hackers use techniques like phishing or malware to gain access to secure networks. Once inside, they can grab important data—like personal information or trade secrets—and transfer it to their own servers for nefarious purposes. The fallout can be devastating, leading to financial losses and a tarnished reputation for the victims. This threat emphasizes the importance of vigilance and robust security measures in protecting our valuable digital assets.
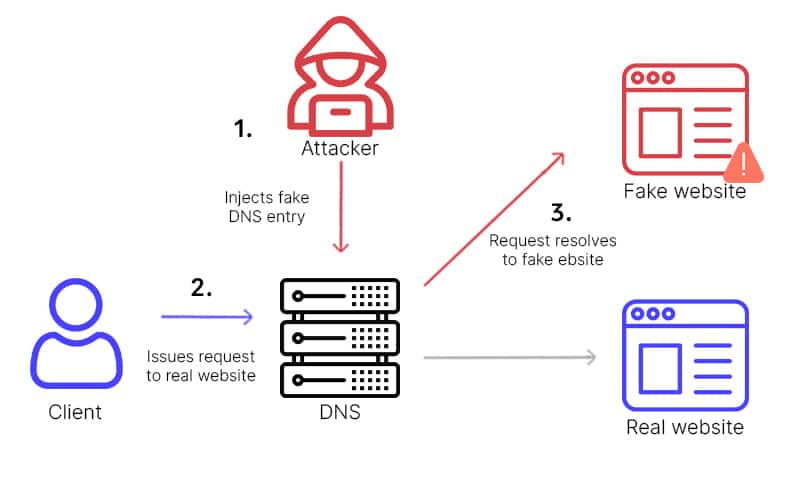
17. DNS Spoofing Attacks:
DNS spoofing attacks, also known as DNS cache poisoning, are a sneaky tactic used by cybercriminals to misdirect users from legitimate websites to counterfeit ones. Imagine typing a familiar web address only to land on a site designed to steal your personal information. Attackers exploit vulnerabilities in the DNS system, tricking it into storing incorrect information. This can lead unsuspecting users to enter sensitive details like passwords or credit card numbers on a fraudulent site, thinking it’s genuine. Such attacks not only compromise personal data but also undermine trust in online services, making it essential to stay vigilant and adopt strong security measures.
18. Cryptojacking:
Cryptojacking attacks happen when hackers covertly take over someone else’s computer or network to mine cryptocurrency without their knowledge. Imagine browsing your favorite website or using an app, only to discover later that your device has been sluggish and your energy bill is higher than usual. In many cases, the culprit is a sneaky piece of code hidden in a web page or software that quietly hijacks your device’s processing power for mining operations. This not only drains your resources but can also lead to overheating and other damage to your hardware. These attacks remind us of the need to stay alert and protect our devices, ensuring that we don’t become unwitting participants in someone else’s profit scheme.
19. Attacks on Critical Infrastructure:
Attacks on critical infrastructure pose a serious threat to our daily lives. Imagine a cyberattack on your local power grid, leaving neighborhoods in darkness and hospitals scrambling to keep essential services running. These attacks disrupt not just electricity but also public safety and economic stability, creating chaos in communities. As cybercriminals become more adept at exploiting vulnerabilities, it’s crucial to prioritize robust cybersecurity measures to protect the essential systems that keep our lives running smoothly.
20. Remote Access Trojans (RATs):
Remote Access Trojans (RATs) are a type of malicious software that hackers use to gain unauthorized access to someone’s computer or network. Imagine opening an email attachment or downloading a file, only to unknowingly invite a digital intruder into your device. Once inside, these sneaky programs can monitor your activity, capture your passwords, and even activate your webcam to spy on you—all without your knowledge. The worst part is that RATs can linger in the background for a long time, quietly collecting your information and allowing cybercriminals to exploit your data. In today’s digital world, where our devices hold so much personal information, being aware of RATs and taking steps to protect ourselves has never been more crucial.
21. Botnet Attacks:
Botnet attacks are a serious cybersecurity threat where cybercriminals hijack a network of compromised devices, known as “bots,” to carry out malicious activities. These devices—ranging from smartphones to smart appliances—can be used without their owners’ knowledge to launch overwhelming Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, steal sensitive data, or distribute malware. As our reliance on connected technology grows, so does the risk of these attacks, emphasizing the need for strong security measures to protect our devices and personal information.

Botnets pose a significant and dangerous cybersecurity threats each year, as they leverage networks of compromised devices to execute large-scale attacks, distribute malware, and facilitate various forms of cybercrime, causing extensive harm to individuals and organizations alike.
22. Web Application Attacks:
Web application attacks are like sneaky break-ins targeting our favorite online services, exploiting weaknesses in their software. By taking advantage of flaws in the code or security settings, cybercriminals can access sensitive data or disrupt services. For example, in a SQL injection attack, harmful code can be entered into a search box to manipulate databases, while cross-site scripting (XSS) allows attackers to run malicious scripts in a user’s browser. With web applications playing such a crucial role in our lives, it’s vital for both developers and users to recognize these threats and take steps to protect their online experiences.
23. Hybrid Threats:
Hybrid threats are complex dangers that combine traditional military actions with unconventional tactics like cyberattacks and misinformation. They exploit weaknesses in both physical and digital spaces, making it hard for nations and organizations to defend against them. For instance, a country might launch a cyberattack on critical infrastructure while spreading false information to sway public opinion. This blending of tactics blurs the lines between war and peace, highlighting the need for a comprehensive understanding of these threats in our increasingly interconnected world.
24. Cyberbullying:
Cyberbullying is a distressing form of harassment that occurs online, where individuals use platforms like social media to engage in hurtful behaviors, such as spreading rumors, sending threats, or sharing embarrassing content. This relentless form of bullying can invade the safe spaces of victims, making them feel isolated and fearful, as it can happen anytime and anywhere. Unlike traditional bullying, the anonymity of the internet often emboldens the aggressors, while leaving victims struggling with feelings of anxiety, worthlessness, and loneliness. It’s vital for friends, families, and communities to promote kindness and support, ensuring that no one faces this painful experience alone.

Cyberbullying remains a pervasive and dangerous cybersecurity threats every year, affecting individuals across all age groups and leading to severe emotional and psychological consequences that can last a lifetime.
25. Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs):
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) are like stealthy intruders that infiltrate digital systems and remain undetected for extended periods. Unlike typical cybercriminals seeking quick financial gain, APTs often have motives like political or corporate espionage. They meticulously research their targets, using sophisticated tactics such as tailored phishing emails and disguised malware to gain access. Once inside, they quietly gather sensitive information, posing a significant risk of long-lasting damage. Understanding APTs is crucial for individuals and organizations, as awareness is the first step in defending against these elusive cybersecurity threats.
Conclusion:
As we navigate the challenges of 2024, it is crucial to remain vigilant against the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity threats. By understanding these attacks and implementing robust security measures, individuals and organizations can better protect themselves from potential harm. Education and awareness play a vital role in safeguarding sensitive information and ensuring a safer digital environment. Remember, cybersecurity is a shared responsibility, and staying informed is the first step in defending against cyber threats.
#cyber attacks 2024 #cybersecurity attacks in 2024 #cyberseurity threats 2024